![TORONTO, ONTARIO-WEDNESDAY OCTOBER 8, 2025—FINANCE—Pedestrians walk across Front Street at Bay Street in Toronto, Wednesday October 8, 2025. [Photo Peter J. Thompson/National Post] [Financial Post Story by TBA for Financial Post] TORONTO, ONTARIO-WEDNESDAY OCTOBER 8, 2025—FINANCE—Pedestrians walk across Front Street at Bay Street in Toronto, Wednesday October 8, 2025. [Photo Peter J. Thompson/National Post] [Financial Post Story by TBA for Financial Post]](data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyB3aWR0aD0iMSIgaGVpZ2h0PSIxIiB4bWxucz0iaHR0cDovL3d3dy53My5vcmcvMjAwMC9zdmciPjwvc3ZnPg==)
Numbers can tell a story. Canada is home to
41.58 million people
, according to the latest population estimates, and the
average age was 41.7.
At the time of the last census, just over half were women and girls, and just under half were men and boys. Of the nearly 30.5 million people 15 and older,
100,815
(0.33 per cent) were transgender or nonbinary. The average household size was 2.4 people.
Five per cent
of the population — 1.8 million people — self-identified as Indigenous. Almost
one-quarter
, or 8.4 million people, were immigrants, many hailing from the three leading places of birth: India, the Philippines and China. Of the
450-plus ethnic
or cultural origins reported, “Canadian” was tops at 5.7 million people.
The
last census
conducted by Statistics Canada in 2021, and released in stages throughout 2022, revealed the ways Canada stands out among the G7, including fastest population growth (mostly due to people moving here from elsewhere), most educated workforce (again, thanks in large part to immigrants), highest proportion of common-law couples and, at almost one-quarter, the highest proportion of foreign-born people who are now citizens.
In December, it was
revealed
that Canada’s population decreased for the first time in about five years — thanks again to immigration or, rather, a drop in its numbers. Driven by caps on international students and temporary foreign workers, the country’s population as of Oct. 1, 2025, declined by roughly 76,068 people, or 0.2 per cent, from July 1, when the population was estimated to be 41.65 million.
The story the numbers tell is just how diverse a country Canada is, and the ways that diversity continues to grow. So, who is Canada now? It’s impossible to answer in the singular.
“Canada has always been a country of diversity. We’ve always been a country with multiple nations, multiple languages, multiple ethnicities, multiple sources of newcomers,” says political sociologist Howard Ramos, a Western University professor. “I don’t think it’s a matter of saying, ‘Who is Canada?’ It’s some kind of plural version of the question: Who are Canadians?”
Lauren Bialystok, an associate professor at the University of Toronto’s Ontario Institute for Studies in Education, expresses a similar sentiment: “Canada is so hard to pin down, and that’s our strength — and it’s also a big challenge.”
Immigration patterns are shifting with nearly
two-thirds of recent immigrants born in Asia,
including the Middle East. Nearly 70 per cent of Canadians — just over 25 million people — reported being white, making the population
the majority
almost everywhere in the country, except for Vancouver (42 per cent), Toronto (40.7 per cent), the Northwest Territories (37.9 per cent) and Nunavut (10 per cent).
More than 95 per cent of visible minorities (non-white and non-Indigenous) lived in one of Canada’s 41 large urban centres. Toronto was home to the largest populations of South Asian, Chinese, Black, Filipino, West Asian, Latin American, Southeast Asian and Korean people, while the country’s largest share of the
Arab population
(35.5 per cent of that group) lived in Montreal.
Indigenous peoples were the
fastest-growing group
, with an eight per cent increase in people identifying as First Nations, Inuit or Métis between 2016 and 2021, compared with 5.4 per cent growth for the non-Indigenous population. They were also the youngest population group, with 41.2 per cent of Indigenous people under the age of 25 compared to 27.3 per cent of the non-Indigenous population.
Canadians are losing their religion like never before. More than one-third (roughly 12.6 million people) reported
being non-religious
, a proportion that more than doubled in 20 years (16.5 per cent in 2001 to 34.6 per cent in 2021). Most religious Canadians reported being Christian, at 53.3 per cent, but their numbers are shrinking, down from 77.1 per cent in 2001. Meanwhile, the proportion of the population who identified as Muslim (Islam was the second-most reported religion), Hindu or Sikh more than doubled in 20 years.
Canada’s aging population is accelerating. There are now more Canadian seniors 65-plus (8.1 million) than children 14 and under (6.3 million), according to
2025 population estimates.
Population aging goes hand-in-hand with fertility, and in 2024, Canada’s fertility rate reached a record low of 1.25 births per woman. Most of the country’s population growth — roughly 97 per cent — is through immigration. As society continues to age, immigration is expected to drive
100 per cent of growth by 2032
.
Canadians are as likely to couple up now as they were 100 years ago, with 57 per cent reporting they were part of one. Most couples live with a partner or spouse, with (25.3 per cent) or without (25.6) children. But at 29.3 per cent, the most common household is one-person dwellings, which hit an all-time high in the last census.
The census adapts as society shifts and tells us how much we’ve changed as a nation. The 2026 census count will begin in May, with the results likely to roll out in 2027. This year’s
long-form census questionnaire
— sent to 25 per cent of households — will include new content on sexual orientation for those 15 and older — “What is this person’s sexual orientation?” — along with homelessness and general health, among other changes to address data gaps.
People often ask Sébastien Larochelle-Côté, Statistics Canada’s director general of Socioeconomic Statistics and Social Data Integration, “What’s the use of the census?” Take homeownership rates, for example. The census provides information down to the lowest levels of geography, from the country’s largest cities to small towns and rural regions. “And it’s going to be different. It’s a very vast and diverse country. It deserves us to be looking at every corner and telling a story about each one of those places and wonderful areas,” says Larochelle-Côté.
Before we see how we’ve changed in the 2026 census, let’s take a look at who we are now.
(Unless otherwise noted, the source is Statistics Canada’s 2021 Census of Population.)
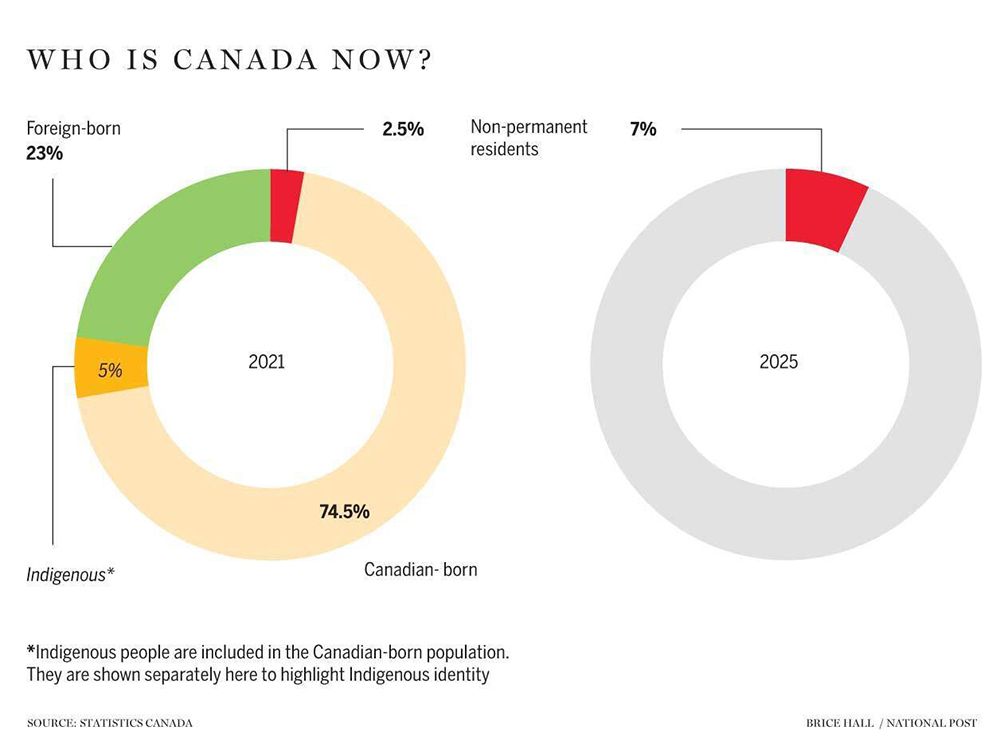
IMMIGRATION
Almost one-quarter (23 per cent) of the population were, or had been, a landed immigrant or permanent resident
Immigration continues to drive Canada’s growth. Nearly one-quarter (23 per cent) of the population were or had been a landed immigrant or permanent resident. Not only was this the highest among the G7, but it was also the largest share since Confederation.
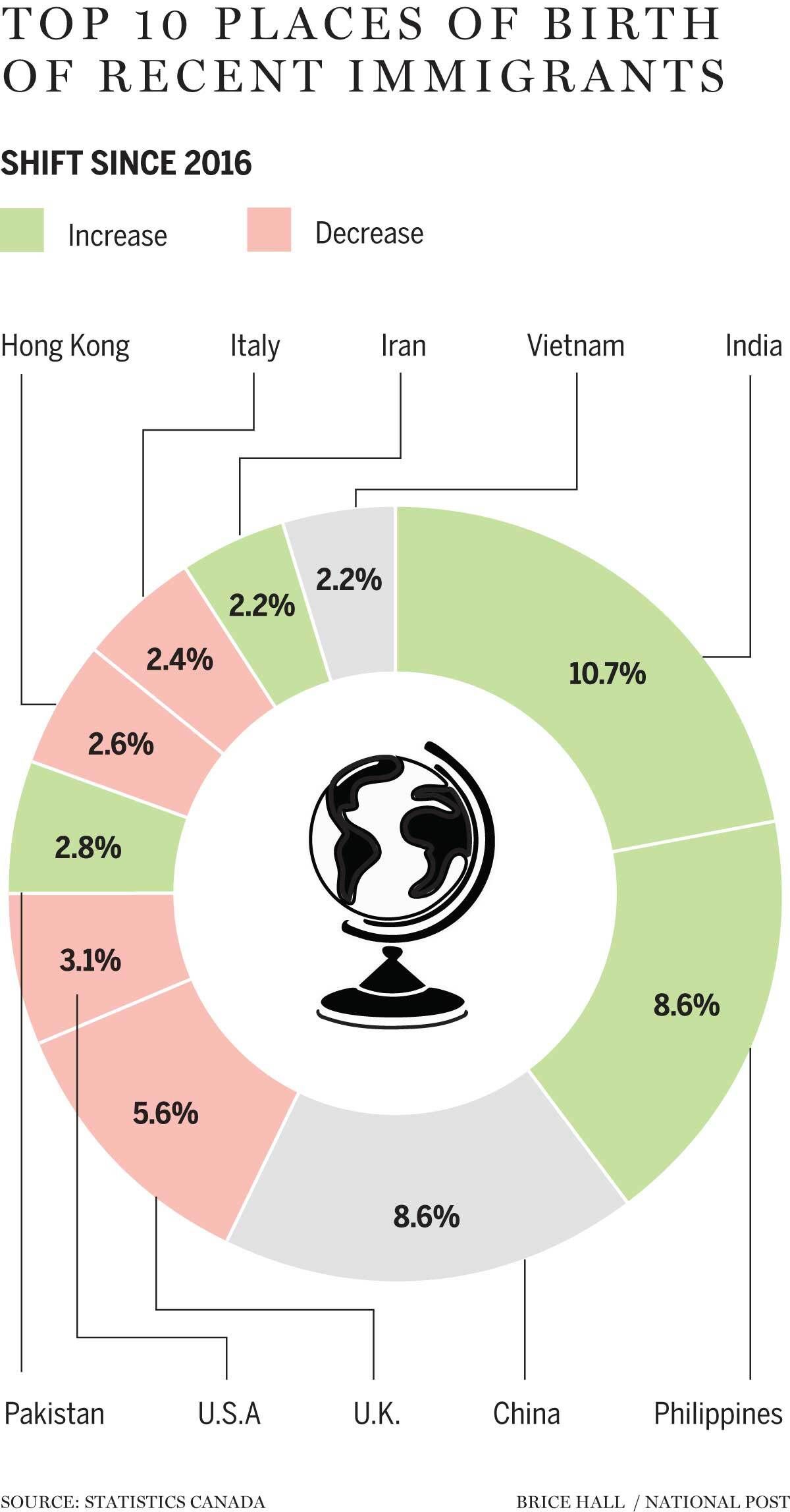
Of Canada’s 8.4 million immigrants, India (10.7 per cent), the Philippines (8.6 per cent) and China (8.6 per cent) were the
top places of birth
.
As
immigration from Europe has declined
over the past 50 years (from 61.6 per cent in 1971 to 10.1 per cent in 2021), the share of new immigrants from Asia, including the Middle East, has increased. Asia is the leading continent of birth for new immigrants (62 per cent), and India is the top country, with nearly one in five (18.6 per cent) recent arrivals from there.
Most of the 1.4 million Southern Asian immigrants were from India (898,050), Pakistan (234,105), Sri Lanka (136,240) and Bangladesh (70,090). Of the one million immigrants born in Southeast Asia, the Philippines (719,580), Vietnam (182,095), Malaysia (25,060), Cambodia (23,065) and Thailand (17,410) were the top countries of origin. The majority of the 1.2 million Eastern Asian immigrants were from China (715,835), Hong Kong (213,855), South Korea (138,355), Taiwan (65,365) and Japan (30,870).
Of the 749,415 immigrants born in West Central Asia and the Middle East, Iran (182,940), Syria (97,595), Lebanon (95,730), Iraq (84,130) and Afghanistan (62,450) were the top five countries of origin.
The mix of where immigrants come from reflects fertility rates and excess population in other countries around the world, says Ramos. Canada used to be among a handful of countries trying to attract talented newcomers. The United Nations now projects that immigration will be the main source of population growth in 52 countries through 2054, including Canada.
“I’m very interested in the 2026 census, whether we see a bigger share of newcomers, not only from India, but also from some of the African countries, such as Nigeria, Ghana or Tanzania, that also have highly educated populations and would be viable economic migrants,” Ramos says.
As a demographer and associate professor at the University of British Columbia, Nathanael Lauster is also excited to see the 2026 census immigration data. “It does give us a much better picture, and a more holistic picture, of how immigration patterns have been reshaping Canada.”
Immigration used to primarily be a story of three cities — Montreal, Vancouver and Toronto — and, to a lesser extent, Calgary and Edmonton, says Larochelle-Côté. Today, Atlantic Canada is increasingly a draw, with the proportion of recent immigrants moving there nearly tripling in 15 years (from 1.2 per cent in 2006 to 3.5 per cent in 2021). “Is this going to begin to be more of a factor in smaller metro areas, for example?” says the StatsCan director, pondering the upcoming 2026 census.
In 2024, more than two in five newborns (42.3 per cent) had a foreign-born mother
Another way Canada’s population growth is tied to immigration is through the number of babies born to mothers from elsewhere, which is increasing the fertility rate.
Immigrants have more children than native-born people, though at fewer than two births per woman, they still have lower than replacement-level fertility, says demographer and sociologist Rachel Margolis, a professor at Western University. “So, it’s not solving our fertility crisis, but it’s increasing, on average, our fertility.”
According to a November 2025 Statistics Canada study,
more than two in five
(42.3 per cent) newborns in 2024 had a foreign-born mother. The report notes that without immigration, Canada would have had negative population growth since 2022.
“Immigration is really fuelling not just population growth, but also the economy, because immigrants are generally younger than the average Canadian. The average Canadian now is 41, and immigrants tend to be younger,” says Margolis.
Since the last census, “Canada became a migration country, not an immigration country,” says Ramos, referring to the number of
temporary residents
— largely international students — outpacing permanent ones. Temporary or non-permanent residents are foreign nationals permitted to stay in Canada for a limited time for study, work or asylum.
With the 2026 census, “We’ll be able to unpack temporary residents versus permanent residents and immigrants,” he adds. “Within the window between the two censuses, there was that growth, but there’s also been a curbing back of the admission numbers, the levels. So, it’ll be interesting to see how that pans out.”
ETHNOCULTURAL & RELIGIOUS DIVERSITY
Canadians reported more than 450 ethnic or cultural origins
The Canadian census has measured people’s origins and religions since 1871. In the most recent one, the population reported more than 450 ethnic and cultural origins, 200 places of birth, 100 religions and 450 languages. Among these origins, alone or with others, “Canadian” took the top spot at 5.7 million, followed by “English” (5.3 million), “Irish” (4.4 million), “Scottish” (4.4 million) and “French” (4.0 million).
Canada’s religious makeup is swiftly changing. Historical data shows that the country was once 97 per cent Protestant and Catholic, says Margolis. “Now, because the religious composition of immigrants is so different from the religious composition of native-born people, we’re seeing really fast increases in the Muslim community, in the Sikh community and the Hindu community, and this has really big implications for everything. I think that’s part of the story about how immigration is changing Canada and Canadian families.”
Just over
half the population reported a Christian religion
(53.3 per cent), down significantly from 77.1 per cent in 2001. With 10.9 million people, Catholics were the largest denomination of Christians.
In the last census, roughly 335,000 people
reported
being Jewish by religion — a slight increase from 330,000 in 2001, but a smaller share of the overall population due to population growth: 1.1 per cent in 2001 to 0.9 per cent in 2021.
However, the census also counts people who identify as Jewish by ethnicity, regardless of their religious affiliation:
282,000 people reported “Jewish” as their
ethnic or cultural origin
, some of whom didn’t identify a religion or reported a religion other than Judaism.
Islam was the second-most common religion after Christianity — nearly 1.8 million, or one in 20, people reported being Muslim. The share of the population who reported being Muslim, Hindu or Sikh has more than doubled since 2001, rising from 2.0 to 4.9 per cent for Muslims, from 1.0 to 2.3 per cent for Hindus and from 0.9 to 2.1 per cent for Sikhs.
“In Canada, religion has become an important variable that’s at the centre of a lot of debates,” says Ramos, who notes that religion is also on the 2026 long-form questionnaire. “So, if you look at, for example, some of the secularization legislation in Quebec, it’s front and centre to public debates there.” He adds that the religious landscape is shifting with the country’s immigrant composition.
“When we look at some of the discrimination that’s been experienced over the last five years (or) post-October 7, as well as longer than that, 9/11, we see that religion becomes quite important, and it often intersects with newcomers from different parts of the world,” says Ramos.
Yet, overall, more than one-third (roughly 12.6 million people) of Canadians reported being non-religious, a proportion that has more than doubled in 20 years (16.5 per cent in 2001 to 34.6 per cent in 2021).
AGING & FERTILITY
More than one in five (21.8 per cent) persons of working age were aged 55 to 64
The age of the working population reached an all-time high, and more than one in five (21.8 per cent) of those Canadians were aged 55 to 64. “You’re talking about your workforce. So that means that these people are essentially thinking about their retirement,” says Larochelle-Côté.
“You have one-fifth of the Canadian population. One-fifth means one-fifth of your economic output, one-fifth of your productivity, one-fifth of your corporate experience, one-fifth of everything, looking at the exit door.”
Nearly one in five (19 per cent) — seven million people — were 65 or older in 2021, an increase of 16.9 per cent since 2016. The age group will grow to nearly one-quarter in 10 years. Over the next 25 years, the population
aged 85 and older could triple
to almost 2.5 million people, as the baby boomers turn 85.
Population aging has wide-ranging effects, says Margolis. “This is the first time that I feel like all of Canada’s problems aren’t economic problems. They’re actually demographic problems.”
Supporting an ever-aging population has implications for health care, housing and the economy, she says. “When more money goes to support older people, we have less money for things that go to younger people. Like our daycare programs, our primary schools, our secondary schools, our labour force training programs, our universities, etc.,” says Margolis.
“These are all really important economic issues around aging, and Canada has chosen to deal with them by trying to solve our population’s potential decline with immigration. But all of these demographic and economic issues (are related).”
Canada’s total fertility rate reached a record low of 1.25 children per woman in 2024
Low fertility causes population aging, says Margolis. “It leads to smaller cohorts of young people, and you end up having a greater proportion of the population that’s old relative to young.” Now in Canada, there are more people aged 65 and over than under 14.
In 2024, Canada’s
total fertility rate
reached a record low of 1.25 births per woman. A century ago, Canadians had, on average, just over three children. The fertility rate increased in the 1950s to nearly four kids. In the 1970s, it plummeted to roughly 1.7, where it hovered until the Great Recession hit in the late 2000s.
“There’s been a really big decline just in the last 15 to 18 years,” says Margolis. “And the reason why that’s important is that it took us from kind of low fertility to very, very low fertility. And the problem with very, very low fertility is that without large immigration, it leads to pretty rapid population decline and pretty rapid population aging, which changes the needs of where we put resources.”
Economics is part of the picture — birth rates tend to go down during financial downturns — but there’s also more freedom in how people choose to see their lives, says Margolis. “Younger generations, they say they want fewer kids … They say it’s less important for them to get married than it used to be. And I think that younger people feel more uncertain about what their path is.”
FAMILIES, HOUSEHOLDS & MARITAL STATUS
Multigenerational households grew by 21.2 per cent in a decade
At 83.6 per cent, married or common-law couples form the most common family structure in Canada, with an even split between those without children (41.8 per cent) and those with children (41.8 per cent). One-parent families made up the difference at 16.4 per cent.
But the Canadian family is also becoming more diverse, says Margolis, with more complex living arrangements, such as co-parenting, coming into focus. “There’s so much diversity in how kids live,” says Margolis. “That’s not something that Canadian data measures very well, and it’s a big problem. We have a lot of stepfamilies in Canada. We have a lot of multigenerational households in Canada, and this diversity is not a bad thing.”
Reliable co-parenting figures may be lacking, but there’s excellent data on
multigenerational households
(at least three generations of the same family living together), says Margolis. In the most recent census, 2.4 million people in Canada lived in a multigenerational household, representing 6.5 per cent of all persons living in a private household.
Two-fifths (40.5 per cent) of people in multigenerational households were born outside Canada, and this living arrangement was most common among people with roots in South Asia. According to a 2025 Statistics Canada study, the prevalence of multigenerational households varies widely, with one in four (24.9 per cent) in Nunavut living in one compared to 3.1 per cent of Quebecers.
Some of these are households of choice, adds Lauster at the University of British Columbia. But in many other cases, parents who can’t find housing of their own for reasons including high rent or shortages, have returned to living with their parents and brought their kids with them. “Those are the situations where, if we had more housing, people would be a little bit more free to live the way they want.”
One-person households (29.3 per cent) were the most common type Canada-wide
The proportion of people living alone has reached an all-time high: 4.4 million people, up from 1.7 million in 1981. Even with this increase, Canada had the second-lowest share of one-person households among the G7.
One-person households
(29.3 per cent) were the country’s most common type, followed by couples without children (25.6 per cent) and couples with children (25.3 per cent).
“Solo households have been the most common household type in Canada since 2016,” says Margolis. “You have people living alone at all different parts of the life course for different reasons. So, people are getting married later, and people in midlife might never be married or divorced or separated. And then you have a lot of older people who live alone.”
Most solo households are in older age groups, but they’re on the rise in midlife. The number of people aged 35 to 44 living alone doubled from 1981 to 2021 (five per cent to 10 per cent), while the proportion of women 65 and older living alone has gradually declined, which Statistics Canada attributes to a narrowing in the life-expectancy gender gap.
The areas of the country with the highest and lowest rates of private households are directly related to the availability of affordable housing. Quebec, where rents are lower, had the most (19 per cent). Nunavut, where housing is scarce, had the least (eight per cent).
Roommates were the fastest-growing type of household
The family form is shifting, with alternatives such as
living with roommates
becoming more prevalent. Though they represent just four per cent of all Canadian households, living with roommates (two or more people not in a census family) was the fastest-growing type from 2001 to 2021 (up 54 per cent), a trend Lauster attributes to the housing crisis.
“For many people, that’s an important connection,” Lauster says. “A lot of people actually really value their roommates, really love living in social situations. But certainly, in terms of its rise as a proportion of households overall, we get a real sense that that’s about the housing shortage. That, indeed, a lot more of these people would be living independently if they could afford to do so.”
After climbing since 2001, the share of 20- to 34-year-olds who lived with at least one of their parents has levelled off at more than one-third (35.1 per cent). But Statistics Canada notes there was a shift to older age groups. Nearly half (46 per cent) of young adults who lived with their parents were aged 25 to 34, a 21 per cent increase in 20 years.
Lauster says this is also likely due to the lack of housing. “You can see a very clear relationship, using the census data, between things like local rents and how households are doubling up.”
In an effort to understand the scope of homelessness in areas large and small, two new questions about the issue will be on the 2026 census. The first asks whether people have “stayed in a shelter, on the street or in parks, in a makeshift shelter, in a vehicle or in an abandoned building” over the previous year. The second asks if people have stayed with friends, family or others because they had nowhere else to live.
GENDER DIVERSITY
Canada the first to provide census data on transgender and nonbinary people
Canada made history as the
first country
to collect and publish census data on gender diversity. The 2021 census included a new question on gender for people aged 15 and older and added the specificity of “at birth” to the question of sex.
(Statistics Canada defines gender as “an individual’s personal and social identity as a man, woman or nonbinary person” and sex as “typically assigned at birth based on a person’s reproductive system and other physical characteristics.”)
Bialystok, at the Ontario Institute for Studies in Education, says this inclusion is a step in the right direction from a research perspective, for accurate data collection. “It also sends a signal that this is something the country cares about, that this country is aligned with our peers in prioritizing sex and gender as something that we protect from discrimination and that we consider essential to human rights,” she adds. “How that actually plays out, and what you can and can’t do with statistics and the way the census is actually administered, are separate questions.”
Even in the five years since the last census, there’s been “a real explosion” in the number of terms used to describe people’s gender, as well as the understanding of what those terms mean. Nevertheless, Bialystok says the census content on gender is a good first step. “The intentions are to continue to make Canada a more inclusive and progressive place. It’s not the end of the story. Collecting the information doesn’t, in and of itself, prevent discrimination or make people’s lives better. But it’s an important start.”
Ramos expects one of the biggest stories of the 2026 census to be self-identification shifting as the political climate has moved away from equity, diversity and inclusion. “South of the border, there’s already some evidence that with the Trump administration, fewer people are identifying as trans,” says Ramos. “It’ll be very interesting to see whether that number remains constant or declines, as we see in some of the data that’s coming from the U.S.”
The 2021 census was also the first to provide data on gender-diverse couples, an example of how the census evolves. Twenty years earlier, the 2001 census was the first to include data on same-sex common-law couples; the 2006 census on same-sex married couples. Of the 8.6 million couples in Canada in 2021, 32,205 included at least one transgender or nonbinary person.
The gender-diverse population is younger overall. The share of transgender and nonbinary people was three to seven times higher for Gen Z and millennials than for older groups.
In the last five years, Bialystok says that the number of young people identifying as trans, nonbinary or genderqueer has grown exponentially. “Even people in the field don’t really know how to explain it, but it’s important to capture, and it’s important to understand what this kind of data collection does and doesn’t mean. Because it doesn’t mean that we’ve necessarily identified the essence of people which will stay the same, and somehow, there are five times more trans people now than there were five years ago. What it means is that there are rapidly evolving cultural norms and opportunities for young people, especially, to express their gender in more nuanced ways than they were able to previously.”
The administration of the census matters, perhaps even more in 2026, adds Bialystok. If a parent is filling out the questionnaire on behalf of a youth, there’s a higher likelihood of underrepresentation or misrepresentation.
Bialystok notes that trust is key. “I think Canada is one of the best places in the world to be if you’re trans or something, but you don’t have to look very far — like just look at the U.S. — to see how quickly a crackdown can happen. And if you start offering to the government, ‘I was born this sex, and now I’m this,’ for some people, especially if they’re in other groups that make them vulnerable, I think that would really give them pause. So, it’s not just adults reporting for youth, and people not being out in their families, but it’s people perhaps not wanting to be out to the government or not knowing how the data is going to be used.”
LANGUAGE
One in four Canadians (nine million people) had a mother tongue other than English or French
While English and French are still the main languages — more than nine in 10 Canadians regularly speak one of them at home —
linguistic diversity is growing
. One in four Canadians (nine million people) had a mother tongue other than English and French, a record high since the government added the question to the census in 1901.
From 2016 to 2021, the proportion of people who mainly speak a non-official language at home increased by 16 per cent, from four million to 4.6 million people. South Asian languages such as Malayalam (+129 per cent), Hindi (+66 per cent), Punjabi (+49 per cent) and Gujarati (+43 per cent) experienced the biggest growth, at a rate “at least eight times larger than that of the entire Canadian population,” according to Statistics Canada.
Besides English and French, Mandarin (531,000 speakers) and Punjabi (520,000 speakers) were the most commonly spoken languages at home.
Mandarin was the primary non-official language
in Toronto and Vancouver, where more than one in four people mainly spoke a non-official language at home.
From 2016 to 2021, the number of Punjabi speakers grew by half (+49 per cent), while Mandarin speakers experienced a more moderate increase (+15 per cent), due to shifting immigration patterns.
More than 70 Indigenous languages spoken in Canada
More than
70 Indigenous languages
were spoken at the time of the last census. While the number of people who learned the language as a second language increased — to 27.7 per cent of Indigenous language speakers from 24.8 per cent in 2016 — the number of Indigenous people reporting being able to have a conversation in an Indigenous language declined by 4.3 per cent.
Onowa McIvor Whitinui, a professor and President’s Chair for Research in the University of Victoria’s Indigenous Education department, has worked in language revitalization, policy and planning for more than 20 years. McIvor Whitinui notes that the oldest generation of Indigenous people is the largest group holding Indigenous languages. Anecdotally, communities have reported losing speakers in recent years. At the same time, the bump in the younger generation of Indigenous language learners suggests that education programs are starting to take hold.
“Although it’s sad and it’s hard when our oldest people and those knowledge holders are passing on, the encouragement of seeing an increase in those statistics in that younger generation of learners tells a really important story, too.”
Graphics by Brice Hall / National Post














![TORONTO, ONTARIO-WEDNESDAY OCTOBER 8, 2025—FINANCE—Pedestrians walk across Front Street at Bay Street in Toronto, Wednesday October 8, 2025. [Photo Peter J. Thompson/National Post] [Financial Post Story by TBA for Financial Post] TORONTO, ONTARIO-WEDNESDAY OCTOBER 8, 2025—FINANCE—Pedestrians walk across Front Street at Bay Street in Toronto, Wednesday October 8, 2025. [Photo Peter J. Thompson/National Post] [Financial Post Story by TBA for Financial Post]](https://smartcdn.gprod.postmedia.digital/nationalpost/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/Canada-census-demographics-faith-immigration-main.jpg)


